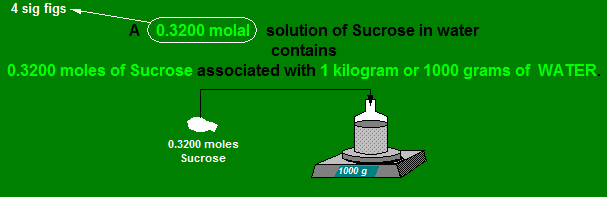
Definition of Molality
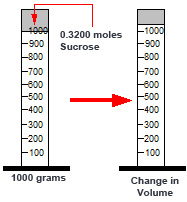
Comment On Volume of Solution
1000g of water has a volume of 1000 ml but the total volume of the Sucrose solution may be over 1000 ml - the Sucrose may contribute to the volume. The overall volume has changed and you cannot predict what the final volume will be.
NOTE: You must take special care if you mix Ethanol and water because the volume will change significantly.
Consider Ethanol
Ethanol dissolving in water is an exothermic reaction which is accompanied by a significant contraction in the total volume. The final volume of the solution is NOT therefore the volume of the water plus the volume of the Ethanol - it is significantly smaller.
Because the volume has changed, any concentrations based on volume must take the change of volume into account eg molarity.
However, because the MASSES of Ethanol and water have NOT changed, concentrations based on weight remain the same eg molality is unaffected.