The problem that you will be shown how to solve is:
"How many millilitres of 20 % w/v Sucrose solution do you need in order to prepare 500 ml of a 10 % w/v Sucrose solution?"
The long approach uses mainly the definition of percent weight in volume:
"Percent weight in volume is the mass - in grams - of a component present in 100 millilitres of the total system".
"How many millilitres of 20 % w/v Sucrose solution do you need in order to prepare 500 ml of a 10 % w/v Sucrose solution?"
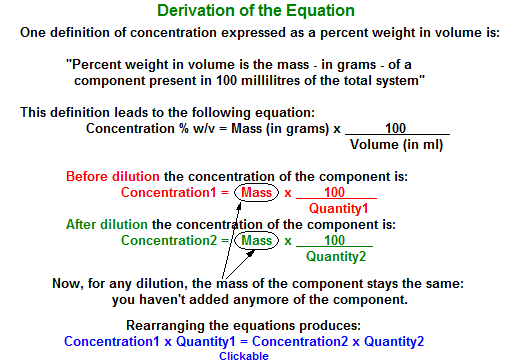
A concentration of 10 % w/ v Sucrose means that:
100 ml of solution contains 10 g of Sucrose. Thus:
500 ml of solution should contain 500 x 10 g = 50 g of Sucrose
100
A concentration of 20 % w/v means that there are:
20 g of Sucrose in 100 ml of solution. Thus:
50 g of Sucrose are in 50/20 x 100 ml = 250 ml of solution.
250 ml of the 20 % w/v solution are needed.
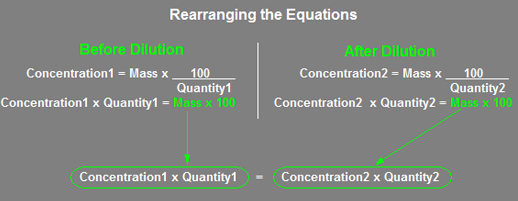
The short approach uses the following equation:
![]()
| Concentration1 | = Concentration of Original Solution |
| Quantity1 | = Quantity (mass or volume) of Original Solution |
| Concentration2 | = Concentration of New Solution |
| Quantity2 | = Quantity (mass of volume) of New Solution |
Click on Equation to Find Out Where It Comes From
"How many millilitres of 20 % w/v Sucrose solution do you need in order to prepare 500 ml of a 10 % w/v Sucrose solution?"

The approaches are those used to find the final concentration of a solution after dilution (or concentration).