Introduction To Antagonists: Theory
Non-Competitive Antagonism: Mode Of Action
Not all antagonists act on the receptors themselves. The production of a response requires a chain of events and some antagonists act on some component of this chain - other than the receptors: disrupt one component and you disrupt the whole chain. For example, see the diagram below:
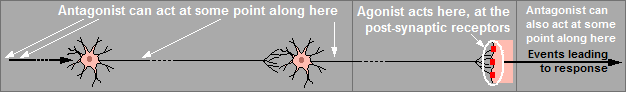
A good example of non-competitive antagonism is seen at autonomic ganglia where some antagonists block the sodium channels. The effect of acetylcholine is therefore reduced in the presence of the antagonists even though the acetylcholine can still interact with the receptors.